Introduction to Digestible Foods
Digestibility plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. The capability of the body to adequately break down and absorb nutrients from the foods consumed is essential for optimal functioning. When food is easily digestible, it can enhance nutrient absorption, reduce strain on the digestive system, and mitigate symptoms associated with common digestive issues.
Digestive discomfort is a prevalent concern, affecting individuals across various demographics. Symptoms such as bloating, gas, and heartburn are often attributed to the consumption of hard-to-digest foods. Stress, poor eating habits, and certain medical conditions can further exacerbate these issues. Thus, choosing the right food groups can significantly alleviate discomfort while promoting overall digestive health.
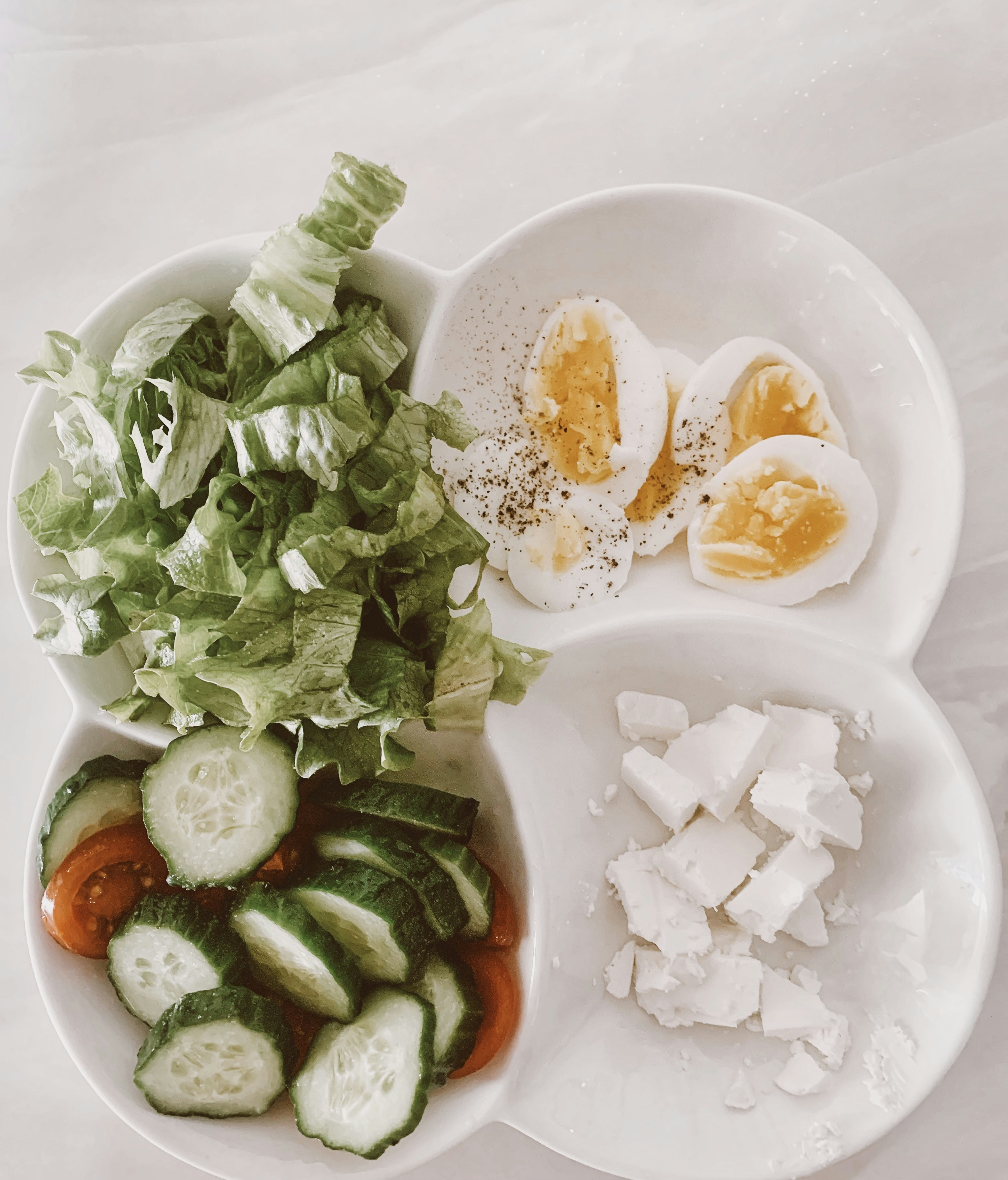
Certain food groups are particularly known for their high digestibility. These groups generally contain fiber, healthy fats, and lean proteins, which support digestive processes. For instance, foods rich in soluble fibers, such as oats and bananas, can help regulate bowel movements and encourage the growth of healthy gut bacteria. Additionally, lean proteins, such as turkey and fish, are easier for the body to break down compared to fatty or heavily seasoned meats. Likewise, low-fat dairy products can offer essential nutrients without burdening the digestive system.
Furthermore, hydration plays a considerable role in enhancing digestibility. Drinking plenty of water and incorporating hydrating foods, like fruits and vegetables, can facilitate smoother digestion. Overall, by opting for easily digestible food groups, individuals can experience a noticeable improvement in their digestive health, ultimately leading to a more comfortable and vital lifestyle.
Fruits and Their Benefits
Fruits play a crucial role in maintaining digestive health, offering various benefits that can enhance overall well-being. Among the numerous fruits available, some stand out for their ease of digestion and positive impact on the digestive system. Bananas, applesauce, and berries are prime examples of fruits that are particularly gentle on the stomach while still delivering essential nutrients.
Bananas are a great choice due to their high soluble fiber content, specifically pectin, which aids in regulating bowel movements. This fruit is also rich in potassium, an electrolyte that helps maintain fluid balance in the body, thereby preventing dehydration. Their soft texture makes them easy to consume, especially for individuals facing digestive discomfort. Consuming ripe bananas can be particularly beneficial as they are easier to digest compared to unripe ones.
Applesauce, another excellent option, offers similar digestive advantages. It provides a source of both soluble and insoluble fibers, contributing to a healthy digestive tract. Applesauce is often recommended for those recovering from gastrointestinal issues because it’s easier to digest than raw apples, while retaining many of the original fruit’s vitamins and antioxidants. The hydration aspect is also significant; incorporating applesauce into one’s diet can help maintain optimal hydration levels, which is essential for digestive health.
Berries, such as strawberries, blueberries, and raspberries, are packed with vitamins and phytochemicals that promote intestinal health. High in antioxidants, berries can help reduce inflammation in the digestive tract. Additionally, their fiber content aids in regular bowel movements, making them an excellent choice in a digestion-friendly diet. Whole berries can be enjoyed as a snack or blended into smoothies for a refreshing and easily digestible option.
In conclusion, incorporating easy-to-digest fruits like bananas, applesauce, and berries into one’s diet not only enhances flavor but also provides significant benefits for digestive health. Their fiber content, hydration properties, and rich vitamin profiles make them indispensable allies in maintaining proper digestion.
Group 2: Soft Grains and Cereals
Soft grains and cereals, such as oatmeal, rice, and quinoa, play a vital role in promoting better digestion. These food groups are known for their gentle impact on the gastrointestinal tract, making them suitable choices for individuals with sensitive stomachs or digestive issues. Nutritionally, they are rich in carbohydrates, providing a quick source of energy without overwhelming the digestive system.
Oatmeal, for instance, is not only versatile but also packed with soluble fiber, which can aid in regulating bowel movements and improving overall gut health. The beta-glucans found in oatmeal can help support healthy gut flora, creating a balanced environment in the digestive tract. This grain is also easy to prepare, requiring minimal cooking time while yielding a comforting meal that can be enjoyed in various forms, from hot bowls to overnight oats.
Rice, particularly white and brown varieties, offers another digestible option. While brown rice contains more fiber and nutrients, white rice is often favored for its easier digestibility. When cooked thoroughly, rice can be soothing to the stomach, providing essential energy without adding stress to the digestive process. It can be served in various dishes, complementing both savory and sweet recipes.
Quinoa, a nutritious pseudo-grain, is another excellent choice. Rich in protein and essential amino acids, quinoa stands out as a complete protein source. Moreover, its gluten-free nature makes it an attractive option for individuals with gluten sensitivities. To enhance its digestibility, it is advisable to rinse quinoa thoroughly before cooking to remove saponins, which can impart a bitter taste. Incorporating these soft grains into your diet can significantly improve digestive health while providing essential nutrients.
Group 3: Lean Proteins
When it comes to promoting better digestion, lean proteins serve as an excellent choice. Among the most recommended sources of lean protein are chicken, turkey, tofu, and fish. These food items are not only lower in fat compared to red meats, but they are also easier for the body to break down, making them more digestible. Understanding the role of these protein sources can significantly impact overall digestive health.
One reason why lean proteins are often easier to digest is their lower fat content. High-fat meats, such as beef and pork, can lead to slower digestion and may contribute to gastrointestinal discomfort. In contrast, lean options like chicken and turkey provide ample protein while minimizing fat intake, facilitating quicker breakdown and absorption. Furthermore, plant-based proteins such as tofu offer an additional digestibility advantage due to their fibrous content, which can aid in the digestive process by promoting regular bowel movements.
The cooking method used also plays a crucial role in the digestibility of proteins. Techniques such as grilling, baking, or steaming tend to preserve the nutritional value of lean proteins while making them easier to digest. Conversely, frying or preparing proteins in heavy sauces can increase their fat content and complicate digestion. Therefore, selecting appropriate cooking methods can enhance the benefit of consuming lean proteins by making them not just nutritious but also gentle on the digestive system.
Moreover, lean proteins provide essential amino acids that are vital for numerous bodily functions, including muscle repair, immune response, and hormone production. This makes them a critical component of a balanced diet. Incorporating a variety of lean proteins into your meals can ensure sufficient amino acid intake while also promoting better digestive health, ultimately contributing to a more balanced lifestyle.
Group 4: Cooked Vegetables
Cooked vegetables play a significant role in promoting digestive health. Cooking methods such as steaming, boiling, or sautéing allow key vegetables, including carrots, spinach, and zucchini, to release vital nutrients while simultaneously breaking down their fibrous structures. This process not only enhances flavor but also makes them easier for the body to digest, thereby alleviating potential gastrointestinal discomfort.
Carrots are particularly beneficial; when cooked, they exhibit increased levels of beta-carotene, which is an essential antioxidant that promotes overall health. Additionally, cooking carrots softens their cell walls, breaking down the harsh fibers that can be difficult for some individuals to digest in their raw form. This transformation of texture permits better nutrient absorption, aiding in smooth digestion.
Similarly, spinach is known for its high concentration of iron and vitamins. When subjected to heat, the oxalic acid present in spinach diminishes, allowing for greater mineral absorption. Cooked spinach is not only gentler on the stomach but also retains much of its nutritional integrity, making it an excellent choice for those seeking digestive ease.
Zucchini is another vegetable that, when cooked, becomes softer and more palatable. This versatility enables it to fit into numerous dishes, providing dietary fiber without causing overwhelming digestive strain. Cooking zucchini helps release its moisture content, which aids in the overall satiety effect without leading to a heavy feeling post-consumption.
Incorporating these cooked vegetables into one’s diet represents a proactive approach to maintaining digestive health. Their ease of digestion, combined with the retention of essential nutrients, establishes them as a favorable group in the pursuit of better digestive wellness.
Group 5: Dairy Alternatives and Fermented Foods
Dairy alternatives and fermented foods play a significant role in promoting better digestion and overall gut health. For individuals who are lactose intolerant, traditional dairy products can lead to discomfort and various digestive issues. Fortunately, there are a number of substitutes available that provide essential nutrients without the adverse effects commonly associated with lactose-containing foods. Almond milk, oat milk, and soy milk are excellent examples of dairy alternatives. These plant-based options are typically easier to digest, making them suitable for those with lactose intolerance, while also being rich in vitamins and minerals.
Fermented foods, on the other hand, introduce beneficial bacteria known as probiotics into the digestive system. Probiotics are essential for maintaining a healthy gut microbiome, which is the community of microorganisms residing in the intestines. Foods such as yogurt and kefir, which are also lactose-free variants available, offer a good source of these probiotics. The fermentation process breaks down lactose, thereby making these foods more digestible for those who may struggle with lactose intolerance. Kombucha and sauerkraut are other noteworthy fermented foods that contribute similarly to intestinal well-being.
The consumption of probiotics can enhance digestion and promote regularity. They help in the breakdown of food and the absorption of nutrients, as well as assist in alleviating symptoms associated with digestive disorders, such as bloating and irregular bowel movements. As individuals explore dairy alternatives and fermented options, it is important to pay attention to the ingredient lists, seeking out those without added sugars or artificial additives. Overall, including these foods in one’s diet can support better digestion and contribute positively to gut health, making them a valuable addition for everyone, particularly those who are lactose intolerant.
Tips for Enhancing Digestibility
Maximizing the digestibility of various foods involves several practical approaches, including cooking techniques, food combinations, and mindful eating habits. By implementing these strategies, individuals can improve their digestive health and ensure that their bodies effectively absorb nutrients.
One effective cooking technique for enhancing digestibility is steaming. Steaming vegetables, for instance, helps to retain their nutritional content while breaking down tough fibers, making them easier to digest. Roasting and sautéing are also beneficial methods, as they can soften food textures without compromising nutrient value. Cooking grains thoroughly can aid in the digestion process, as it breaks down complex carbohydrates into simpler sugars, allowing for easier absorption by the body.
Food combining is another important aspect of improving digestibility. Combining foods that digest at similar rates can prevent discomfort. For example, pairing proteins with non-starchy vegetables rather than starches can enhance the digestive process. This is because starches and proteins require different enzymes for digestion, potentially leading to sluggishness if consumed together. Incorporating fermented foods, such as yogurt or sauerkraut, can also assist digestion by introducing beneficial probiotics, which help balance gut bacteria.
Mindful eating habits can significantly promote efficient digestion. Eating slowly and chewing food thoroughly increases saliva production, which contains enzymes that begin the digestive process. Additionally, being aware of food intolerances is crucial; keeping a food journal can help identify which foods may cause adverse reactions. Staying hydrated is equally important, as water aids in breaking down food and helps move it through the digestive tract smoothly.
Incorporating these practical tips into daily routines can create a more balanced digestive experience, ultimately contributing to overall health and well-being.
Common Digestive Issues and Food Group Solutions
Many individuals experience digestive discomfort, which can manifest as bloating, gas, and constipation. These common digestive issues can stem from various factors, including dietary choices, stress, and lifestyle habits. Fortunately, incorporating easy-to-digest food groups into one’s diet can play a pivotal role in alleviating these problems. Understanding how specific food groups interact with the digestive system is essential for promoting overall gut health.
Bloating is often caused by the accumulation of gas in the gastrointestinal tract, which can result from consuming foods that are difficult to break down. Easy-to-digest food groups such as bananas, avocados, and plain rice are gentle on the stomach and can help reduce bloating. Bananas, rich in potassium, also aid in managing sodium levels in the body, which can further mitigate bloating.
Gas can accumulate as a result of fiber intake, especially from legumes and certain vegetables. By focusing on easily digestible food options such as cooked carrots, zucchini, and sweet potatoes, individuals can reduce gas formation while still obtaining necessary nutrients. Cooking these vegetables helps break down complex fibers, making them less likely to cause discomfort.
Constipation is another prevalent issue that can be exacerbated by a low-fiber diet. To combat this, whole grains like oatmeal and barley, along with fruits such as berries and apples, provide soluble fiber that promotes regular bowel movements. Including these food groups can offer both symptomatic relief and preventive measures against future occurrences of constipation.
Incorporating these five easy-to-digest food groups into one’s daily diet can significantly improve digestive health. Individuals should consider their unique needs and consult with healthcare professionals if necessary, ensuring that they remain aligned with their health goals while actively addressing any digestive concerns.
The Importance of Hydration for Digestion
Hydration plays a pivotal role in the digestive process, facilitating the breakdown of food and the absorption of essential nutrients. Water is not only crucial for overall health but serves specific functions that enhance digestion. Adequate hydration aids in the production of saliva, which contains enzymes that begin the digestion of carbohydrates as soon as food enters the mouth. Furthermore, it assists in moving food smoothly through the gastrointestinal tract, thereby preventing common issues such as constipation and bloating.
Water also helps to dissolve nutrients in food, making it easier for the body to absorb these nutrients during the digestive process. Particularly when enjoying the five easy-to-digest food groups, adequate water intake enhances their digestibility. This means that alongside these food groups, consuming the right amount of hydration becomes fundamental to maximizing nutritional benefits. In addition to drinking plain water, incorporating herbal teas into your routine can provide a soothing effect on the digestive system. Herbal teas, such as peppermint or ginger, are known for their ability to alleviate discomfort and promote gastrointestinal health.
Moreover, hydrating foods—such as cucumbers, watermelon, and oranges—can serve as delicious supplements to standard meals. These foods not only provide valuable vitamins and minerals but also significantly contribute to your daily fluid intake. When consumed with a balanced diet, these hydrating options enhance the overall digestive process. It is essential to maintain a consistent intake of fluids throughout the day to support digestion effectively. In essence, staying properly hydrated contributes significantly to optimal digestive health, ensuring that food is not just eaten but pleasantly and successfully digested.
Conclusion and Final Thoughts
In the quest for optimal digestive health, the selection of food plays a crucial role. Throughout this blog post, we have highlighted five easy-to-digest food groups, each contributing uniquely to improved digestion and overall well-being. By incorporating fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your daily diet, you can create a balanced nutritional intake that not only supports digestion but also enhances your energy levels and overall bodily functions.
Fruits and vegetables are particularly rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, promoting healthy digestive processes while preventing constipation. Opting for whole grains provides necessary nutrients and promotes a sense of fullness, further aiding weight management efforts. Lean proteins, such as fish and chicken, are beneficial for muscle maintenance and repair, while being easy on the digestive system. Healthy fats, from sources like avocados and olive oil, can also facilitate nutrient absorption and provide satiation without causing discomfort.
It is important to remember that individual responses to food can vary. What may be easy to digest for one person could be more challenging for another. Therefore, it is advisable to pay attention to your body’s reactions when trying new foods. Gradually introducing these easy-to-digest food groups into your meals can assist in fine-tuning your diet according to your own digestive needs.
By exploring and integrating these food groups, you empower yourself towards achieving better digestion and enhancing your overall health. A balanced diet rich in easy-to-digest options is a sustainable way to support your digestive system, promoting long-term wellness. Embrace these food choices, and prioritize your digestive health for a vibrant and fulfilled life.